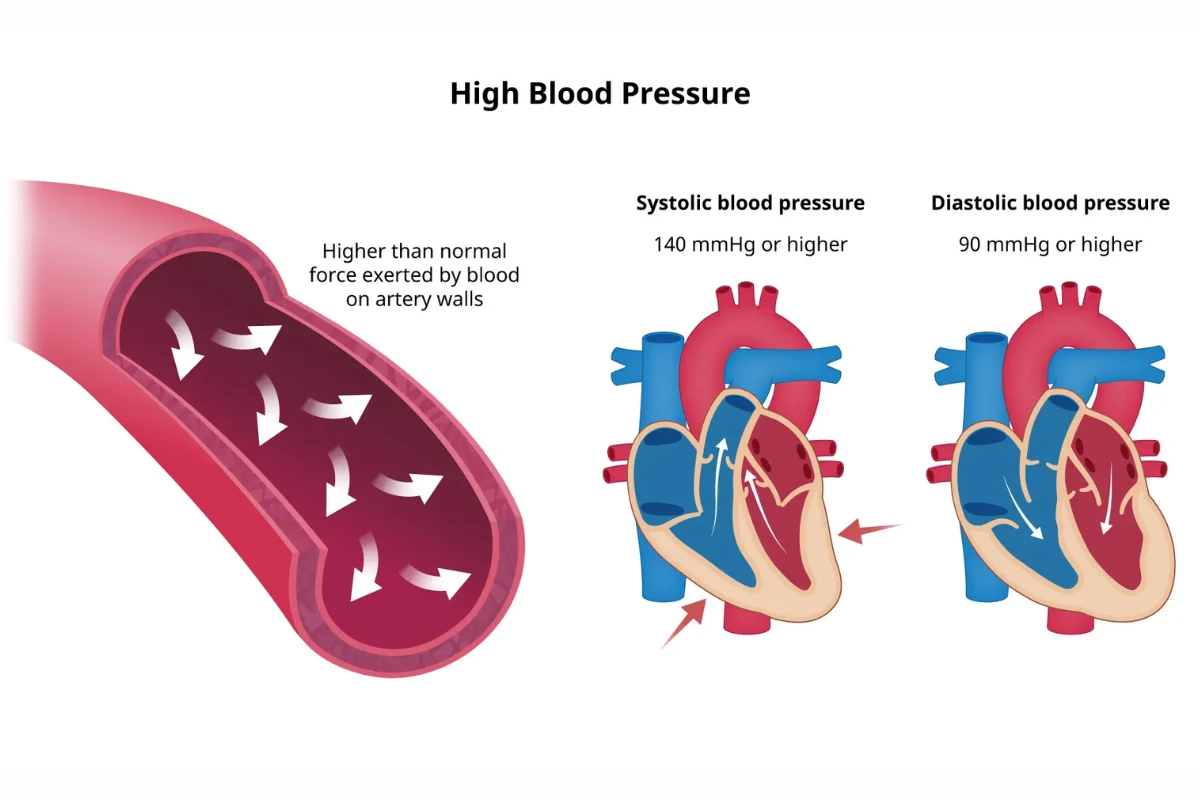
High Blood Pressure
A silent but serious condition where blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. It is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
Cause: Obesity, high salt intake, stress, or genetic predisposition.
Symptoms: Often asymptomatic, but may include headaches, dizziness, or blurred vision.
Complications: Heart attack, stroke, kidney damage, and vision loss.
Treatment: Lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring.
Low Blood Pressure
Low Blood Pressure a condition where blood pressure drops below normal levels, leading to inadequate blood supply to organs. It can cause dizziness and fainting.
Cause: Dehydration, heart conditions, or endocrine disorders.
Symptoms: Dizziness, fainting, blurred vision, and nausea.
Complications: Shock, falls, and organ damage.
Treatment: Increased salt intake, medications, and addressing underlying causes.
Palpitations
A noticeable sensation of the heart beating irregularly, rapidly, or forcefully. While often benign, persistent palpitations may require medical evaluation.
Cause: Stress, caffeine, hormonal changes, or arrhythmias.
Symptoms: Fluttering or pounding sensation in the chest.
Complications: Rarely, may indicate serious arrhythmias.
Treatment: Lifestyle changes, stress management, or medications.
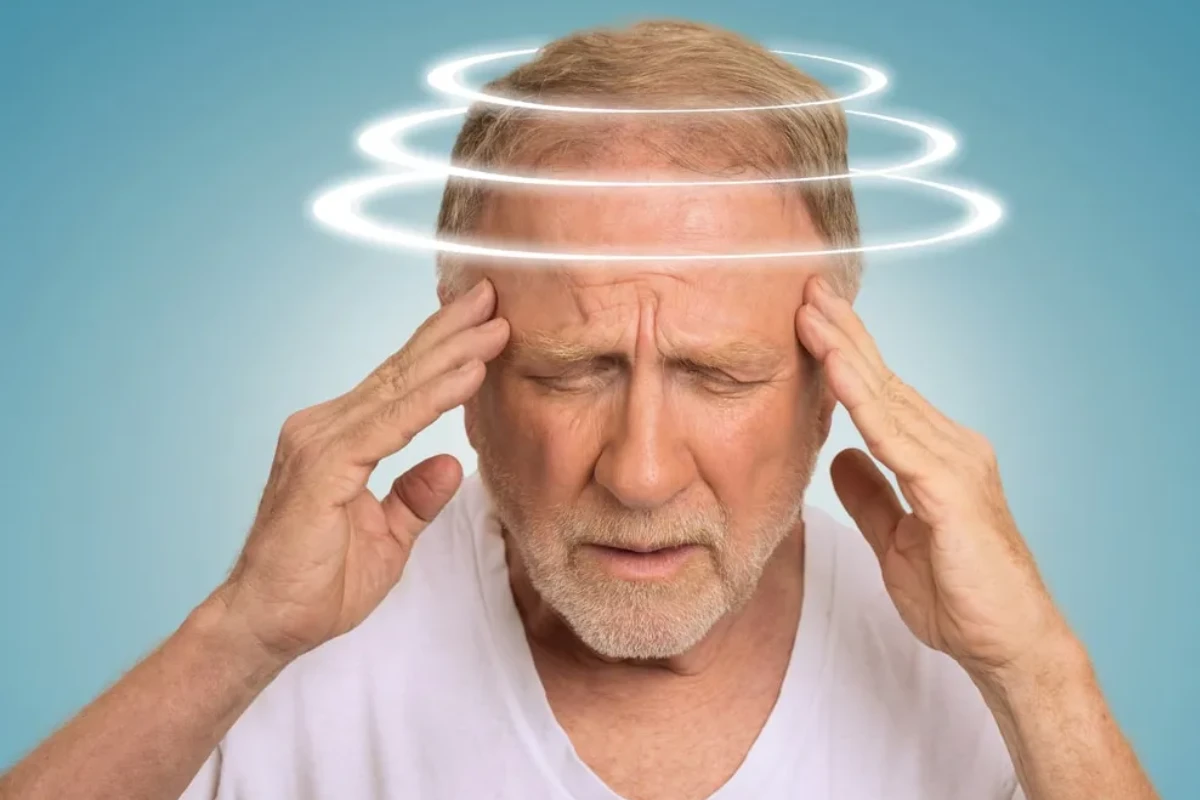


Head Reeling / Sudden Fall
Head Reeling / Sudden Fall a sudden loss of balance or dizziness, which may indicate underlying cardiovascular or neurological issues.
Cause: Low blood pressure, dehydration, or neurological disorders.
Symptoms: Dizziness, fainting, and loss of coordination.
Complications: Falls, injuries, and reduced mobility.
Treatment: Hydration, medications, and treating the underlying cause.
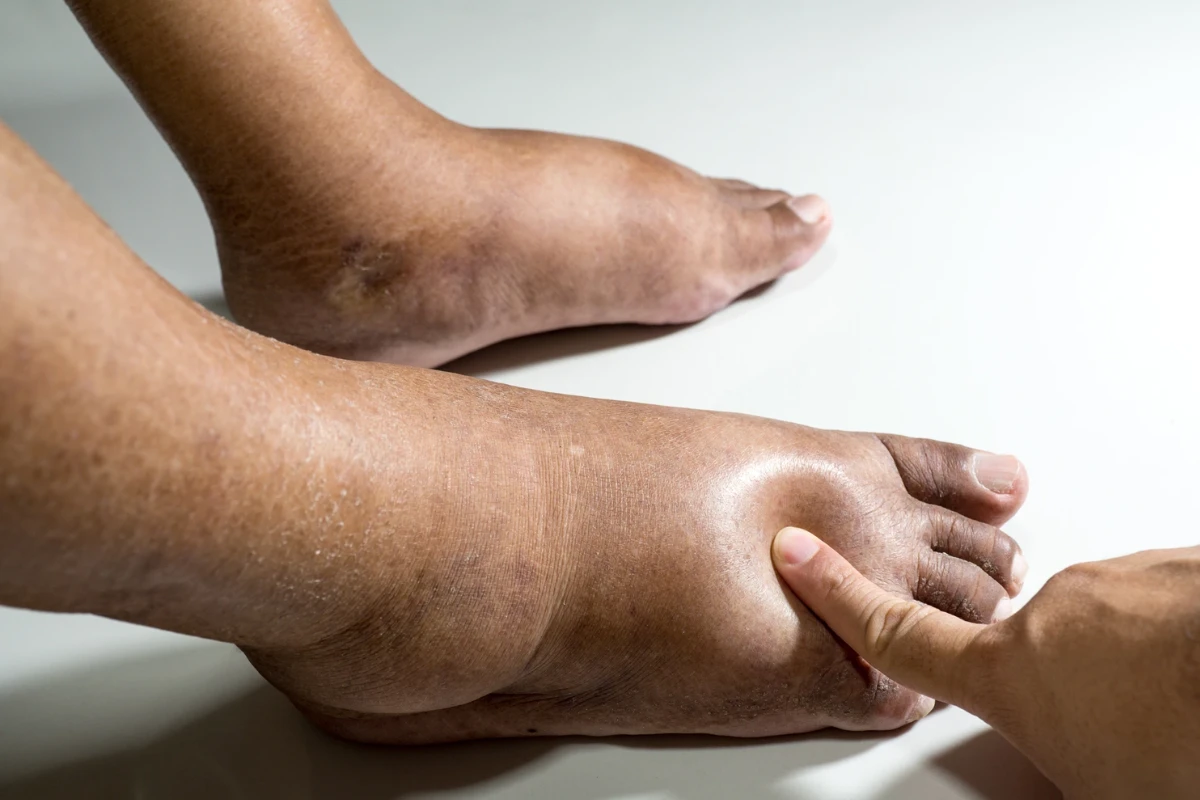
Swelling of Legs
A condition where fluid accumulates in the lower limbs, causing puffiness and discomfort. It may indicate circulation issues, heart disease, or kidney problems.
Cause: Fluid retention due to heart failure, kidney disease, venous insufficiency, or prolonged sitting/standing.
Symptoms: Puffy, heavy legs, skin tightness, and difficulty walking.
Complications: Skin ulcers, infections, and deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Treatment: Lifestyle changes, compression stockings, diuretics, and treating the underlying cause.

Chest Pain
A symptom that can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, often linked to heart disease but also caused by respiratory, digestive, or musculoskeletal conditions.
Cause: Heart attack, angina, acid reflux, lung infections, or muscle strain.
Symptoms: Pressure, tightness, burning, or stabbing pain in the chest, sometimes radiating to the arms or jaw.
Complications: Heart attack, stroke, or respiratory failure.
Treatment: Depends on the cause—may include medications, lifestyle changes, or emergency intervention.
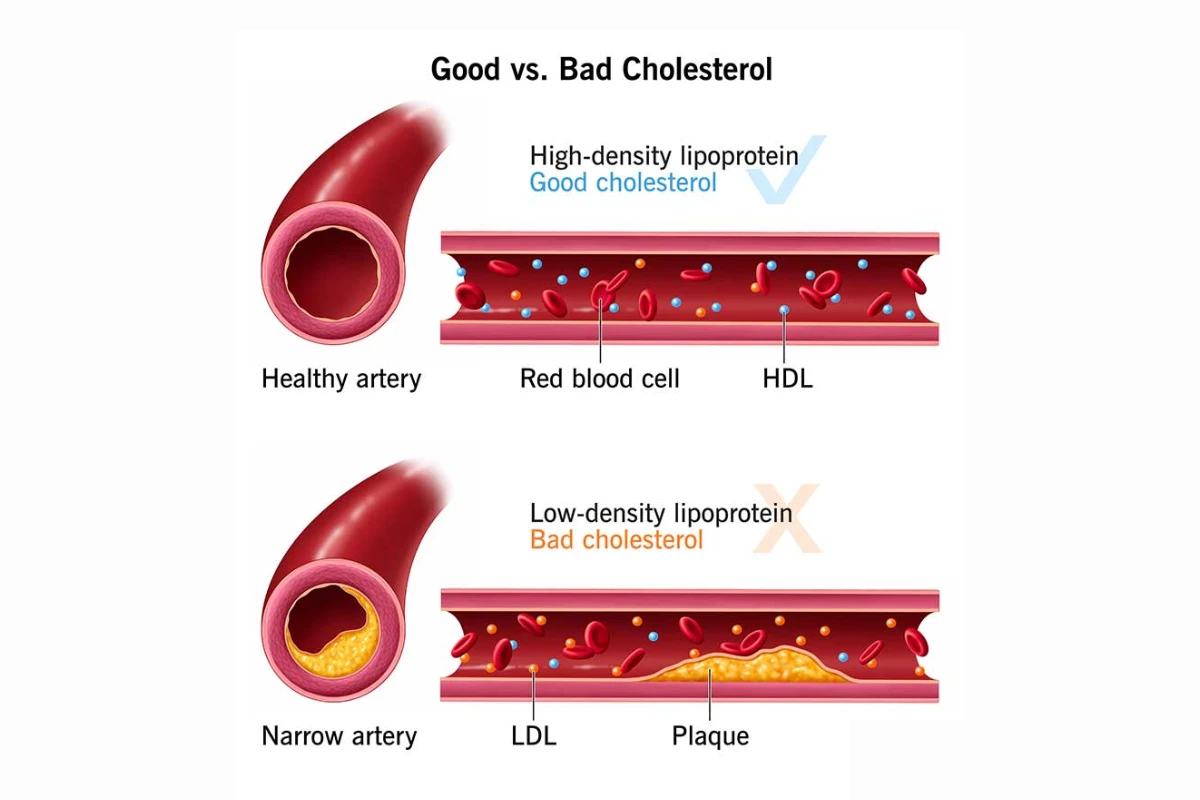
Cholesterol Problems
High or abnormal cholesterol levels increase the risk of heart disease and stroke by contributing to plaque buildup in the arteries.
Cause: Poor diet, genetics, lack of exercise, obesity, and certain medical conditions.
Symptoms: Often asymptomatic, but may cause chest pain or xanthomas (fatty deposits under the skin).
Complications: Atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
Treatment: Lifestyle changes, cholesterol-lowering medications, and regular monitoring.
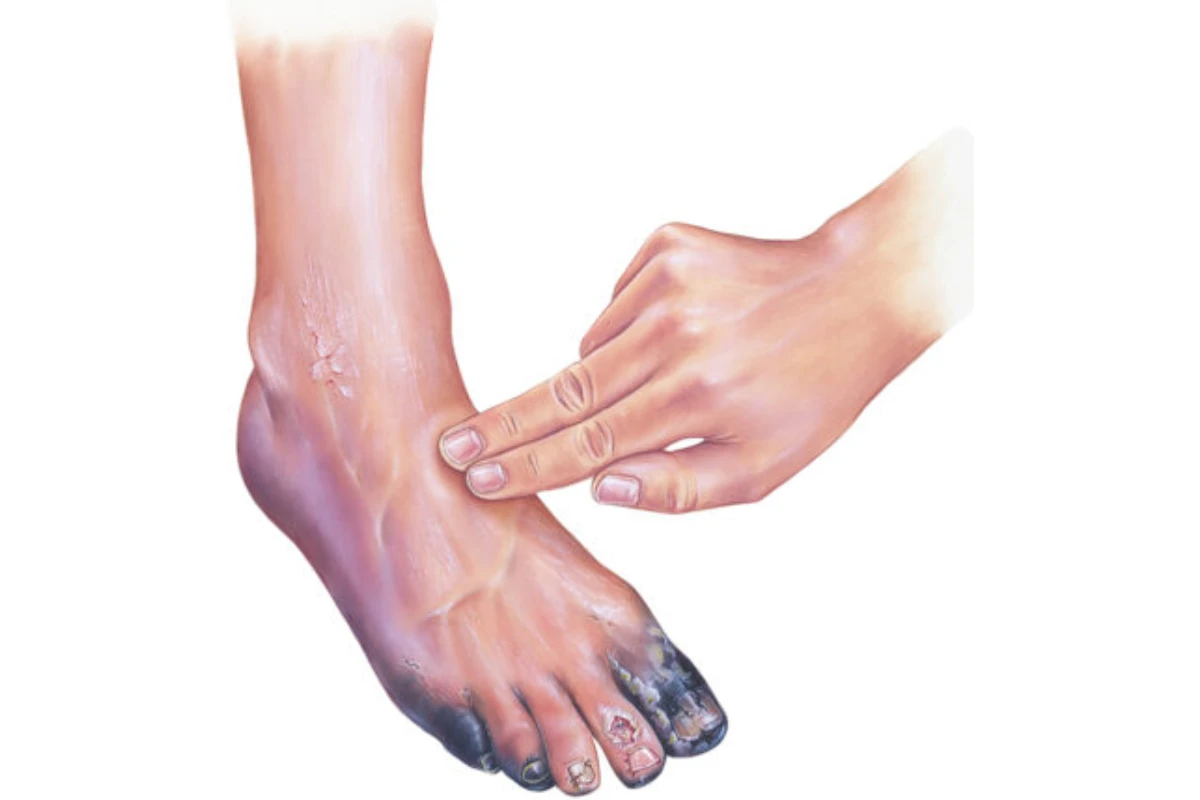
Chronic Limb Ischemia
A severe condition caused by reduced blood flow to the limbs due to arterial blockages, leading to pain and tissue damage. It often arises from advanced atherosclerosis and can result in significant disability if untreated.
Cause: Reduced blood flow to limbs due to arterial blockages, often from atherosclerosis.
Symptoms: Pain in limbs, ulcers, gangrene, and cold or numb extremities.
Complications: Tissue death, infection, and amputation.
Treatment: Lifestyle changes, medications, angioplasty, or bypass surgery.
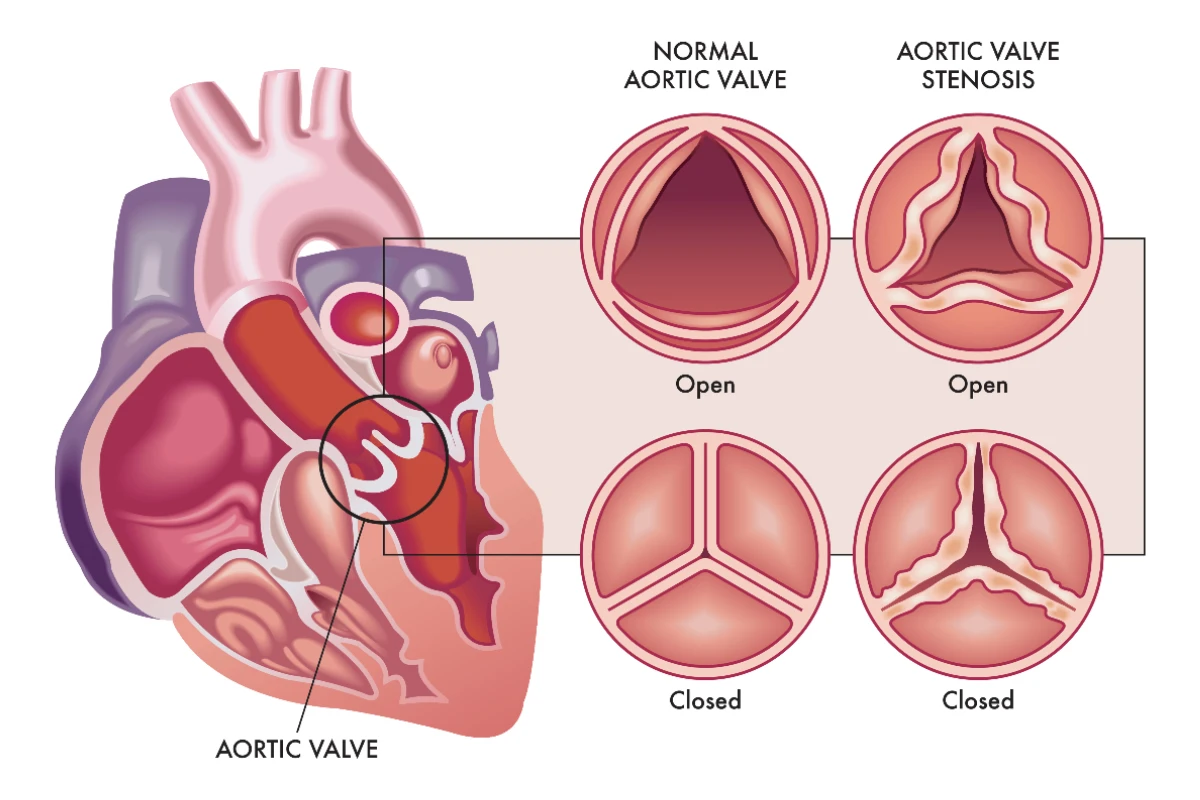
Aortic Stenosis
A narrowing of the aortic valve that impedes blood flow from the heart to the body. It commonly affects older adults and can lead to severe complications like heart failure if not managed promptly.
Cause: Narrowing of the aortic valve due to calcification, congenital defects, or rheumatic fever.
Symptoms: Chest pain, breathlessness, fainting, and fatigue.
Complications: Heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death.
Treatment: Medications, balloon valvuloplasty, or valve replacement surgery.
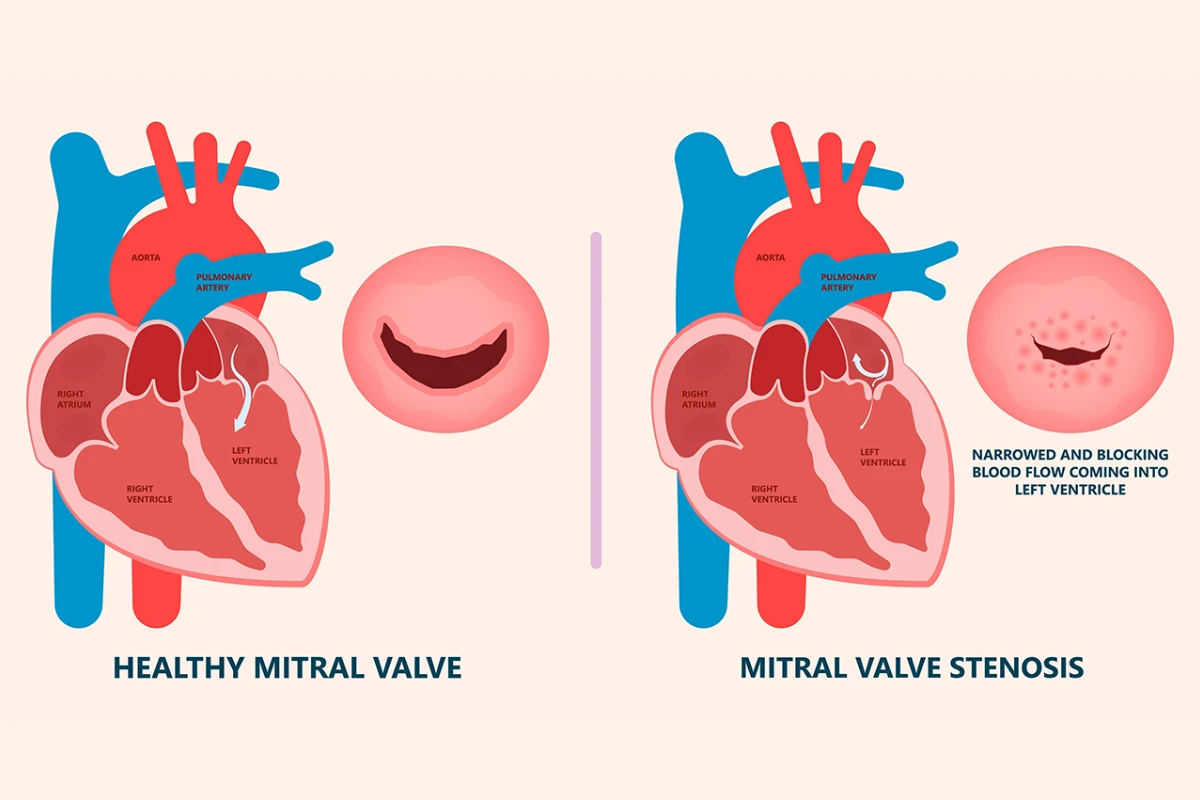
Mitral Valve Stenosis
A condition characterized by the narrowing of the mitral valve, which hinders blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. It is often caused by rheumatic fever and can lead to significant cardiac complications.
Cause: Narrowing of the mitral valve, commonly from rheumatic fever or calcium buildup.
Symptoms: Breathlessness, fatigue, palpitations, and swelling in the legs.
Complications: Atrial fibrillation, stroke, and pulmonary hypertension.
Treatment: Medications, balloon valvuloplasty, or surgical repair/replacement.
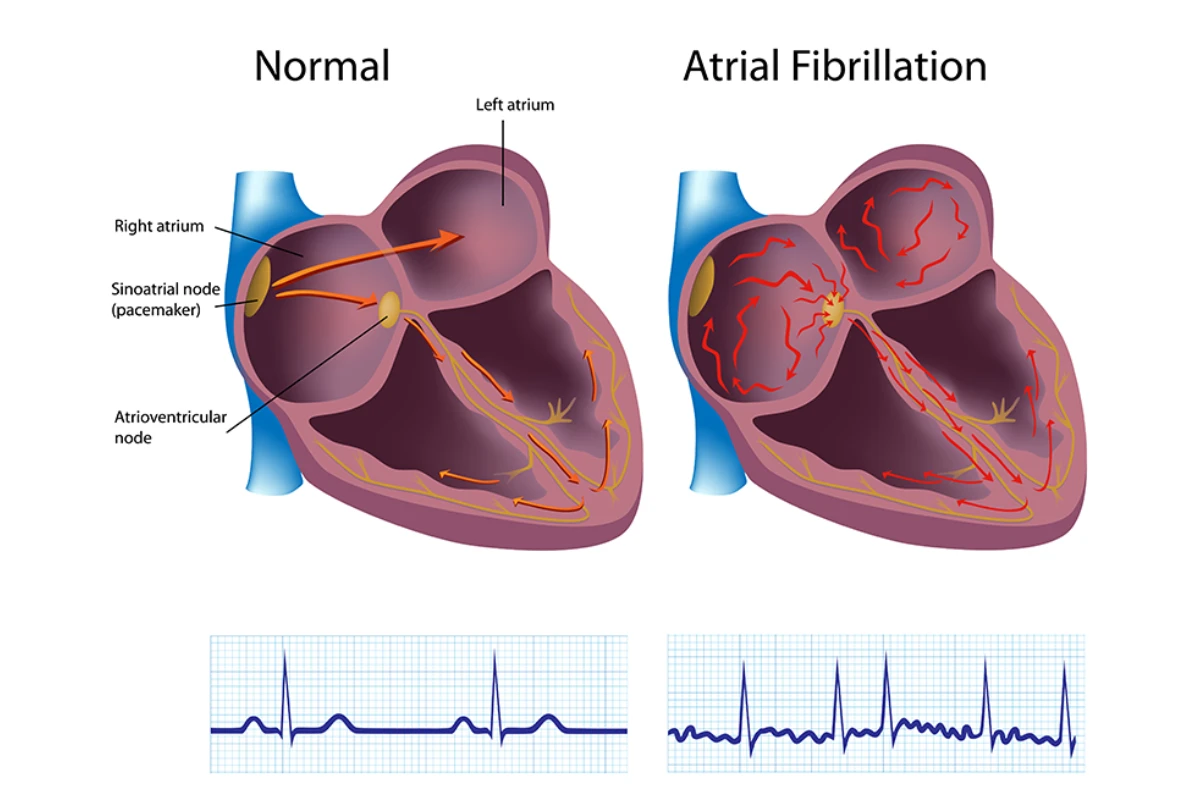
Atrial Fibrillation
A common heart rhythm disorder causing irregular and often rapid heartbeats. It increases the risk of stroke and other heart-related complications if untreated.
Cause: Irregular electrical impulses in the heart, often from hypertension, coronary artery disease, or hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms: Rapid heartbeat, fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Complications: Stroke, heart failure, and blood clots.
Treatment: Medications, electrical cardioversion, or catheter ablation.
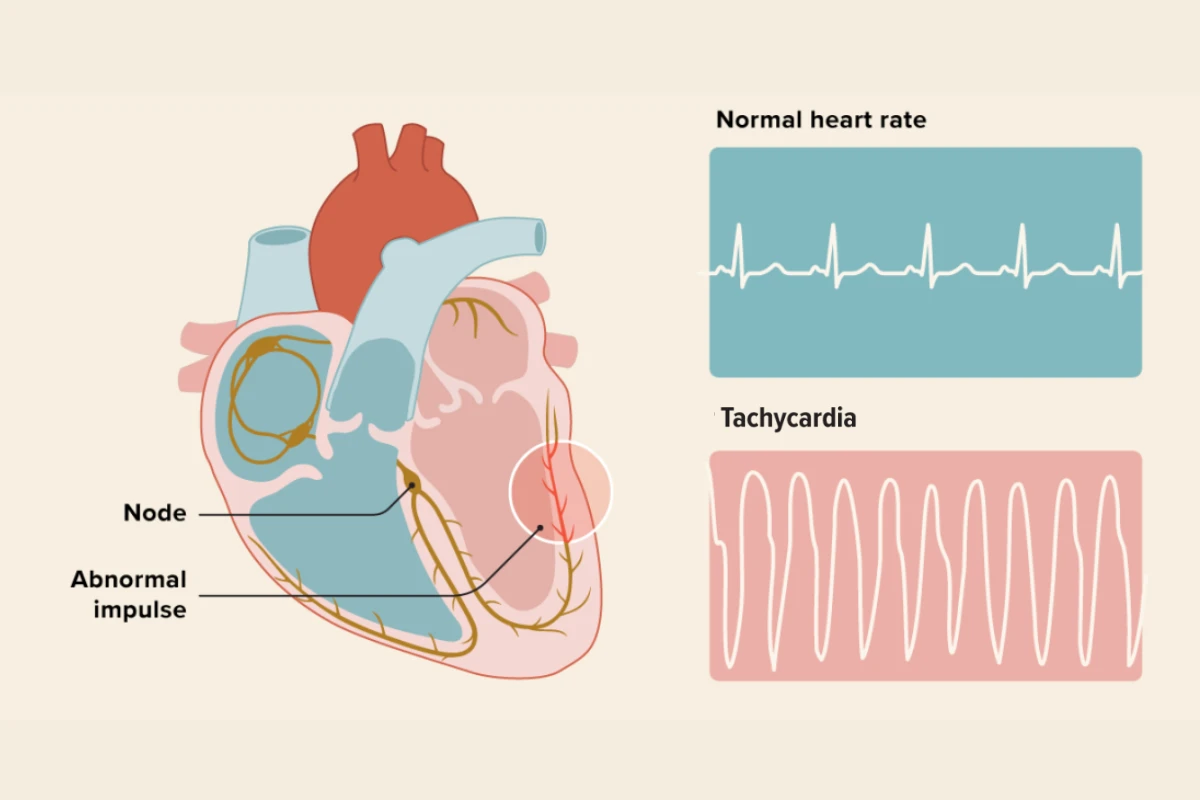
Tachycardia
A condition where the heart beats faster than normal due to various triggers. It can be temporary or a sign of an underlying heart issue.
Cause: Abnormally fast heart rate due to stress, fever, anemia, or heart conditions.
Symptoms: Palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, and fainting.
Complications: Heart failure, stroke, and sudden cardiac arrest.
Treatment: Medications, vagal maneuvers, or ablation therapy.
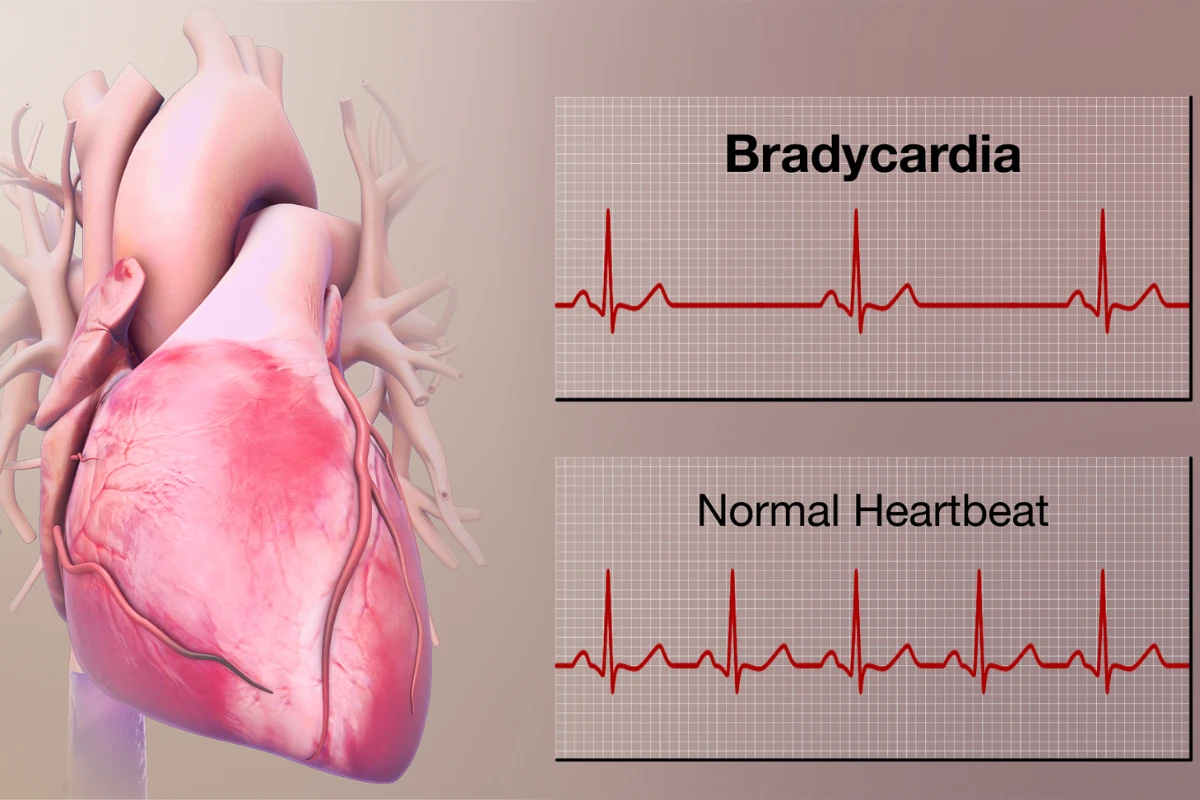
Bradycardia
A slow heart rate that can be normal in healthy individuals but problematic if it leads to insufficient blood flow. It often requires monitoring and, in severe cases, intervention.
Cause: Slow heart rate caused by aging, heart disease, or electrolyte imbalances.
Symptoms: Fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and fainting spells.
Complications: Heart failure, frequent fainting, and sudden cardiac arrest.
Treatment: Medications, pacemaker implantation, or addressing underlying conditions.
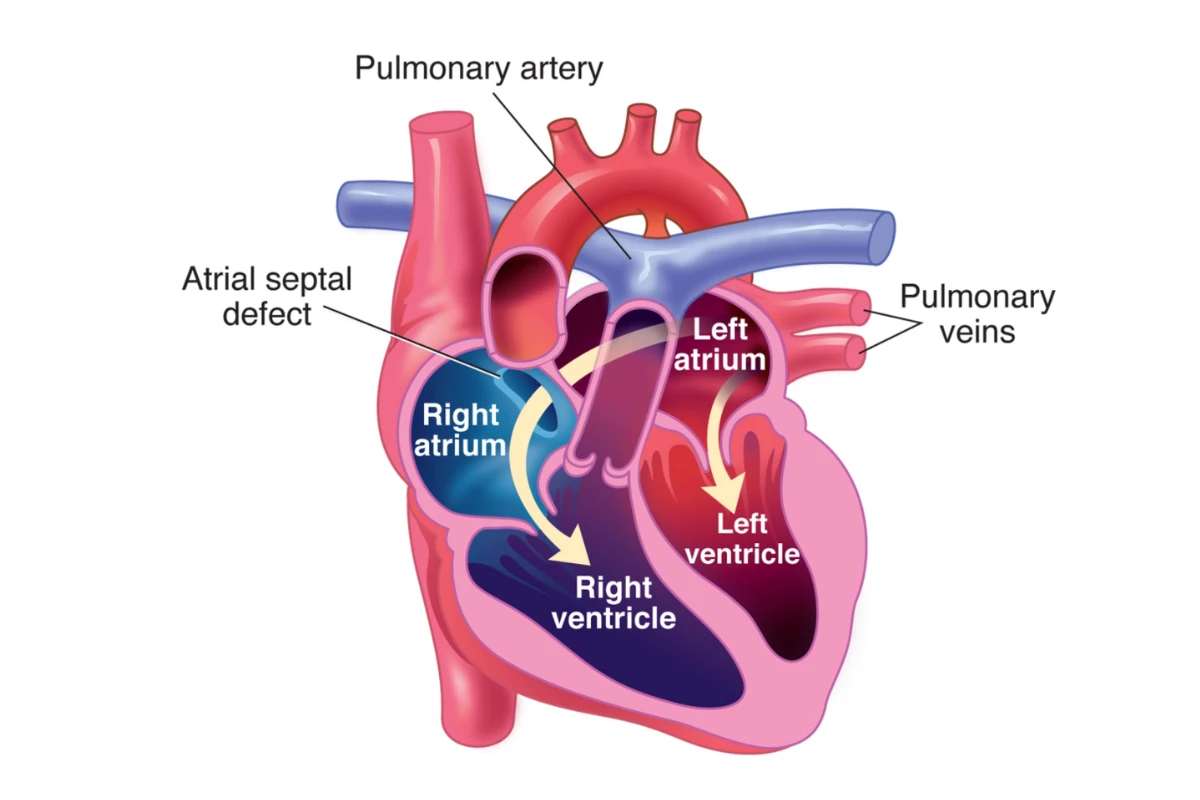
Atrial Septal Defects
A congenital heart defect where a hole in the wall between the heart’s atria allows oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood to mix. It can cause long-term complications if untreated.
Cause: Congenital defect causing a hole in the wall between the atria.
Symptoms: Fatigue, breathlessness, heart murmurs, and frequent respiratory infections.
Complications: Arrhythmias, stroke, and pulmonary hypertension.
Treatment: Monitoring, medications, or surgical repair.
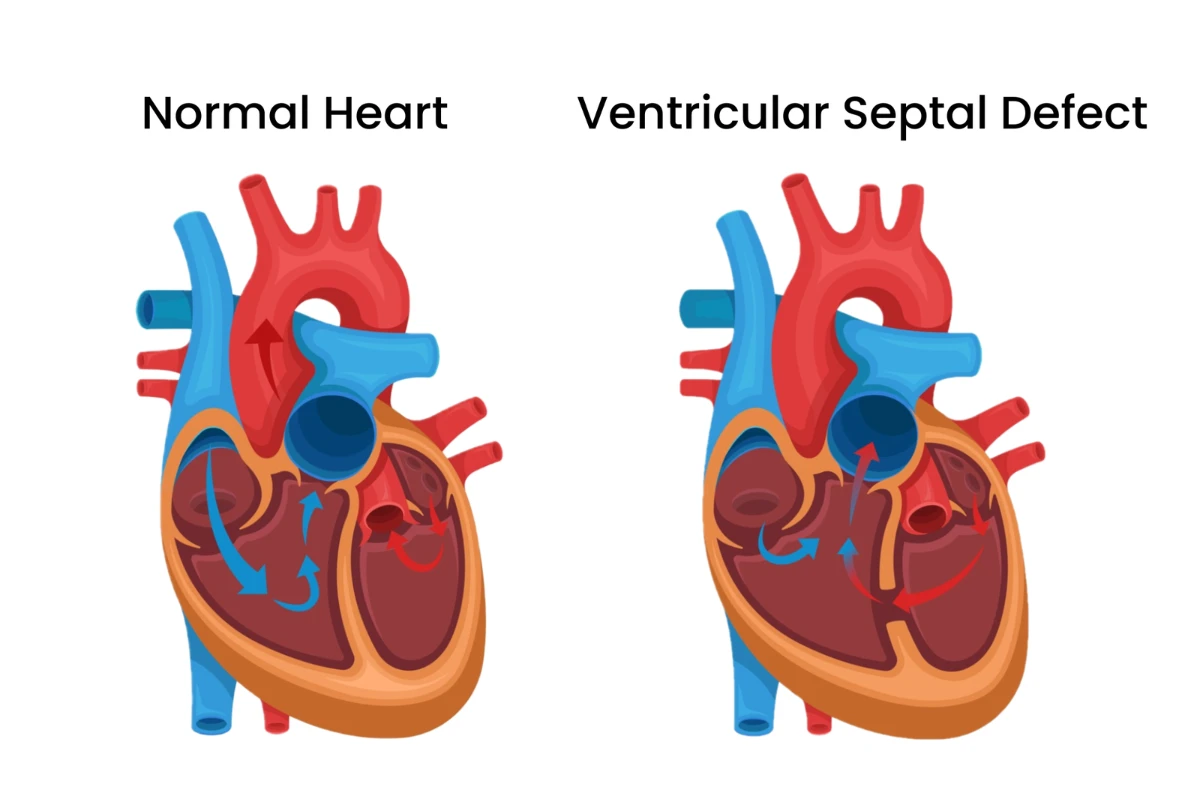
Ventricular Septal Defect
A congenital heart defect involving a hole between the heart’s ventricles. It affects normal blood flow and may lead to heart failure if untreated.
Cause: Congenital defect with a hole in the wall between ventricles.
Symptoms: Fatigue, rapid breathing, poor growth, and heart murmurs.
Complications: Heart failure, infections, and pulmonary hypertension.
Treatment: Medications or surgical repair.
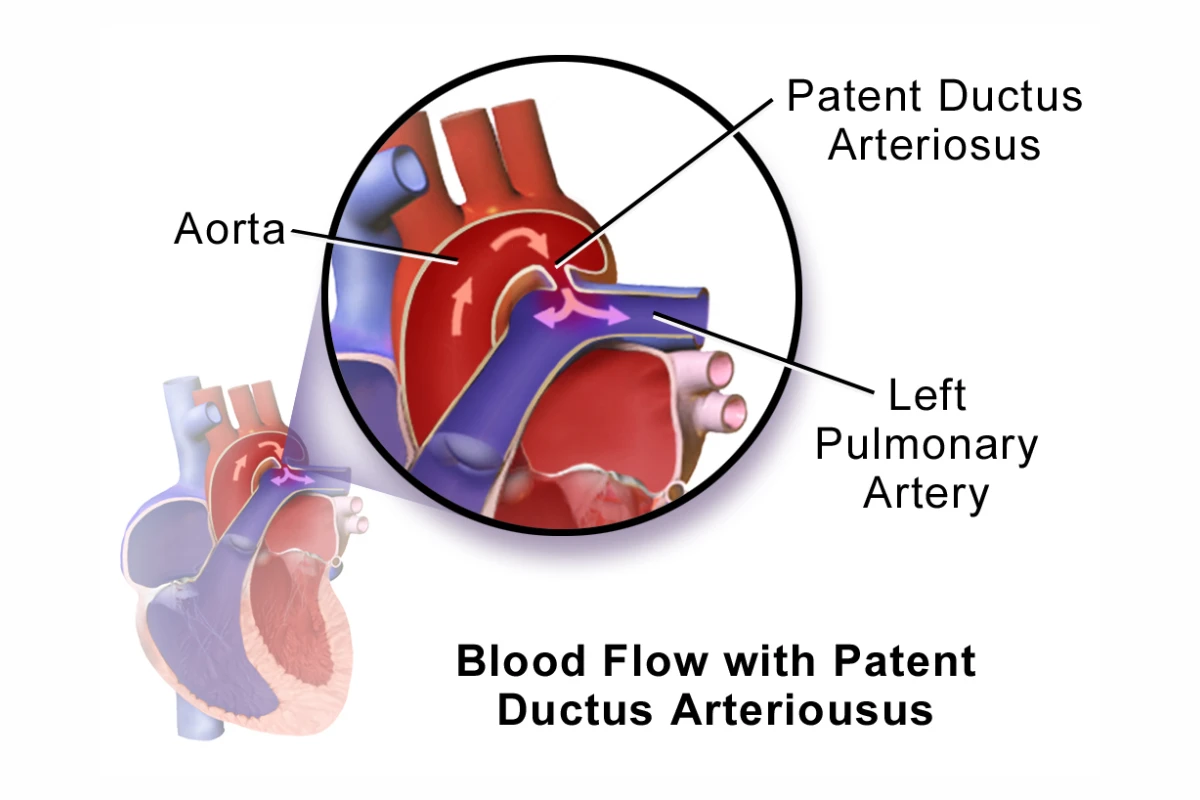
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
A persistent opening between the aorta and pulmonary artery, which is normal before birth but should close shortly after. PDA can strain the heart and lungs if left untreated.
Cause: Persistent opening between aorta and pulmonary artery after birth.
Symptoms: Breathlessness, fatigue, poor feeding, and rapid heart rate.
Complications: Heart failure, infections, and pulmonary hypertension.
Treatment: Medications, catheter-based closure, or surgery.
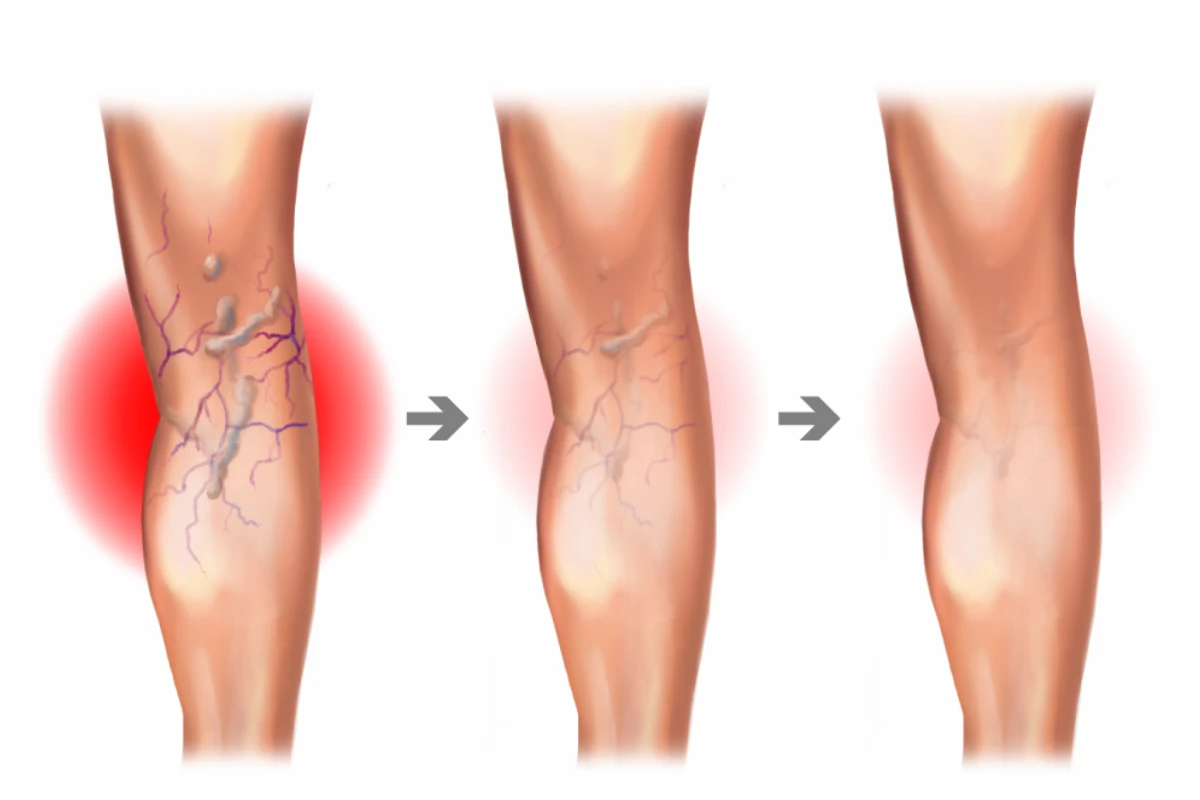
Varicose Veins
Enlarged, twisted veins that commonly occur in the legs. They result from weakened valves and can cause discomfort and aesthetic concerns.
Cause: Weak or damaged vein valves leading to blood pooling.
Symptoms: Swollen, twisted veins, leg pain, and heaviness.
Complications: Ulcers, blood clots, and chronic venous insufficiency.
Treatment: Compression stockings, lifestyle changes, or vein ablation procedures.
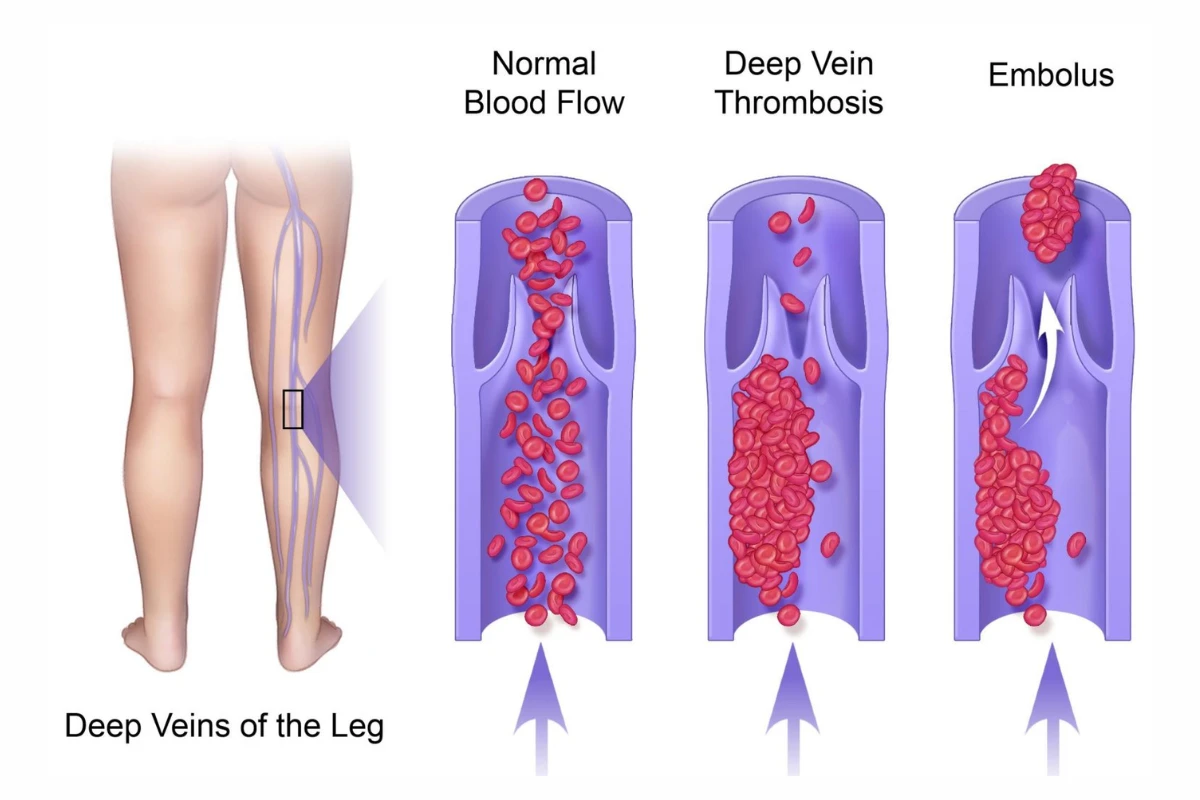
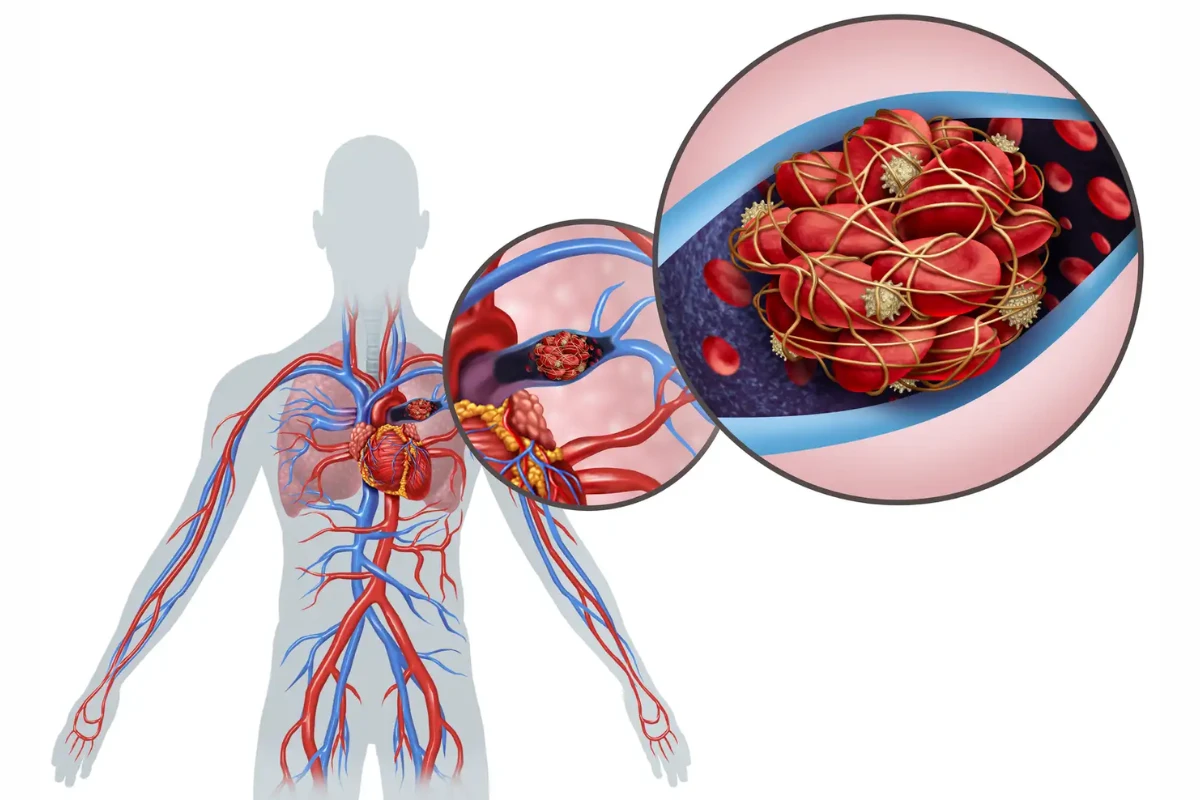
Deep Vein Thrombosis
A serious condition involving blood clots in the deep veins, usually in the legs. It can lead to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism.
Cause: Blood clots in deep veins due to prolonged immobility or clotting disorders.
Symptoms: Swelling, pain, redness, and warmth in the affected limb.
Complications: Pulmonary embolism and post-thrombotic syndrome.
Treatment: Anticoagulants, thrombolytic therapy, or compression stockings.
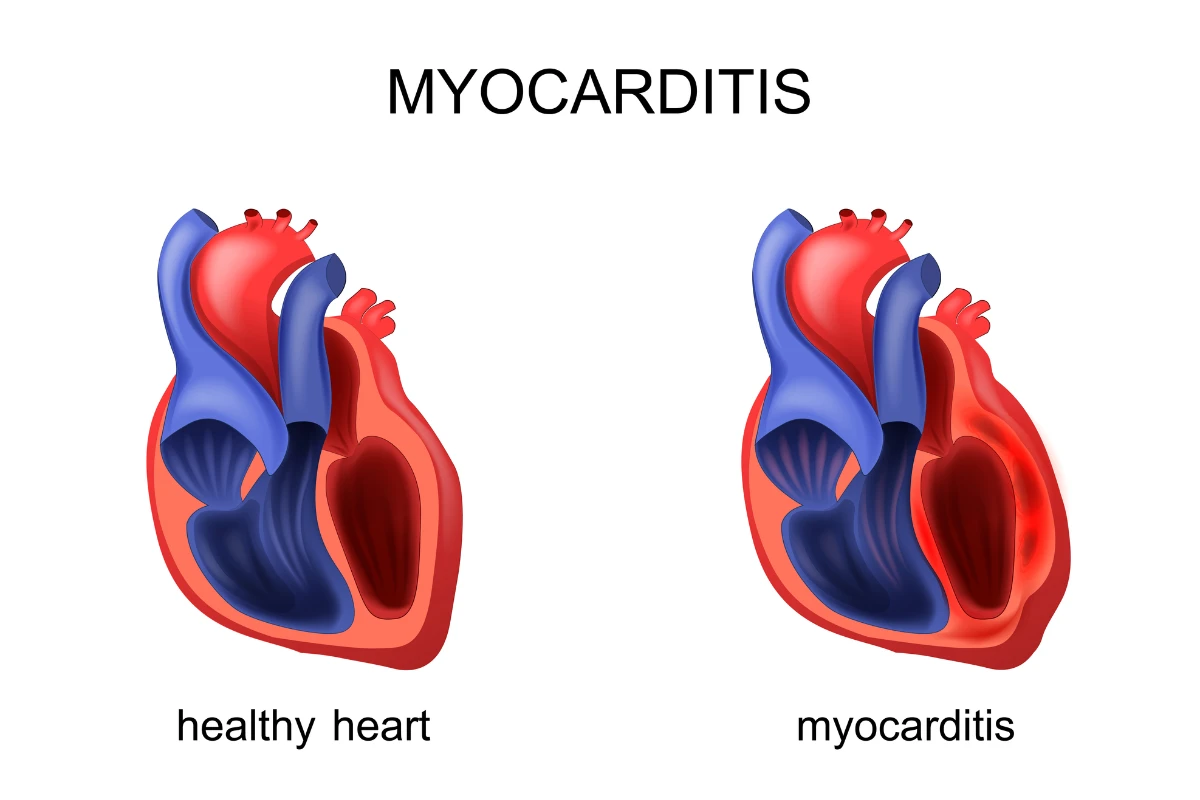
Myocarditis
Inflammation of the heart muscle, often caused by viral infections or autoimmune disorders. It can weaken the heart and affect its ability to pump blood effectively.
Cause: Inflammation of the heart muscle from infections or autoimmune conditions.
Symptoms: Chest pain, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, and breathlessness.
Complications: Heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death.
Treatment: Medications, rest, and treating the underlying cause.
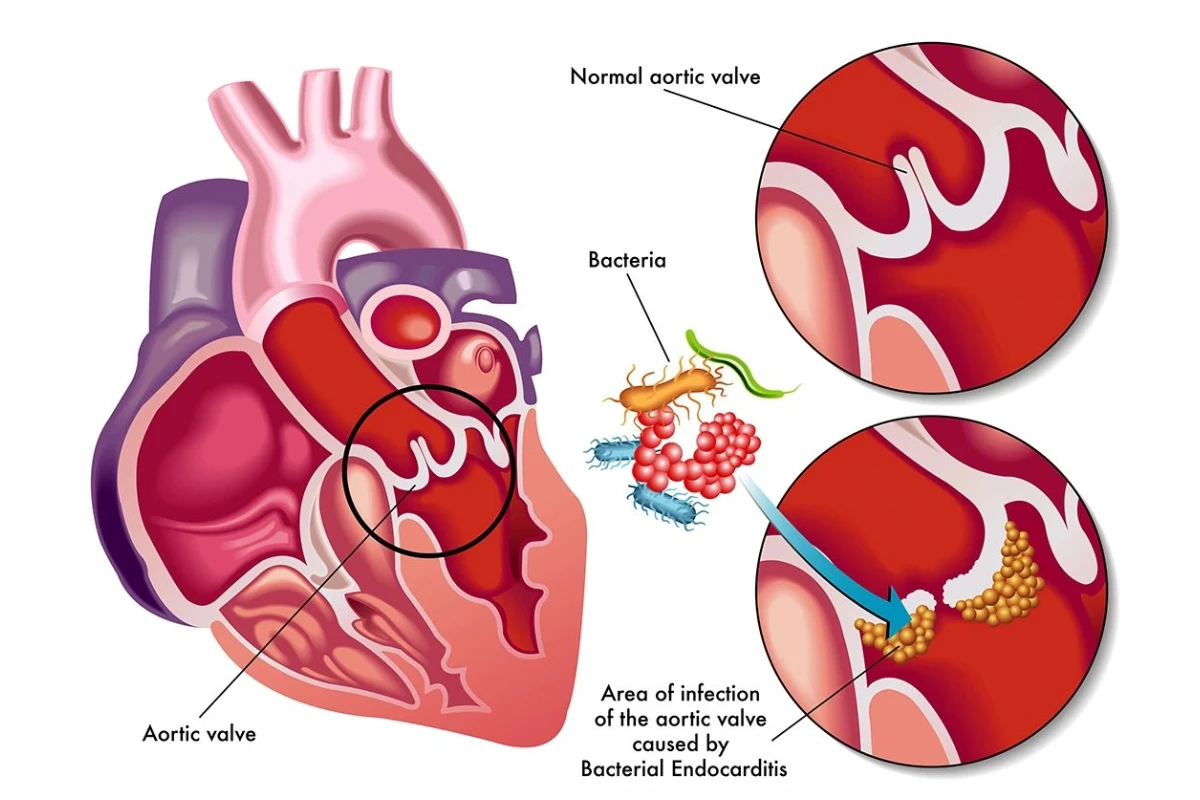
Endocarditis
An infection of the heart’s inner lining, typically caused by bacteria entering the bloodstream. It is a life-threatening condition that requires prompt treatment.
Cause: Infection of the heart lining, often from bacteria.
Symptoms: Fever, fatigue, heart murmurs, and swelling.
Complications: Heart valve damage, stroke, and abscess formation.
Treatment: Antibiotics or surgery in severe cases.
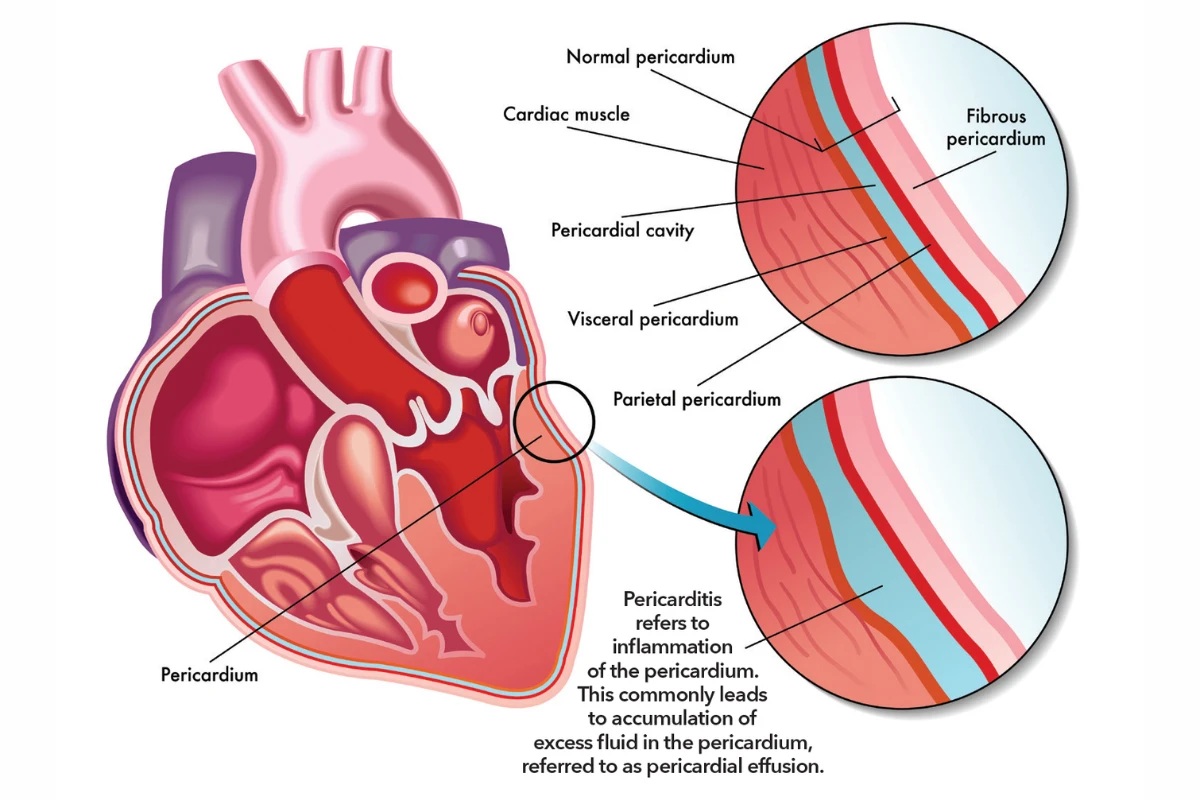
Pericarditis
Inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart, which can cause chest pain and other symptoms. It is often linked to infections or autoimmune conditions.
Cause: Inflammation of the pericardium due to infections, trauma, or autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms: Sharp chest pain, fever, and shortness of breath.
Complications: Cardiac tamponade and chronic constrictive pericarditis.
Treatment: Anti-inflammatory medications, rest, and in severe cases, pericardiocentesis.
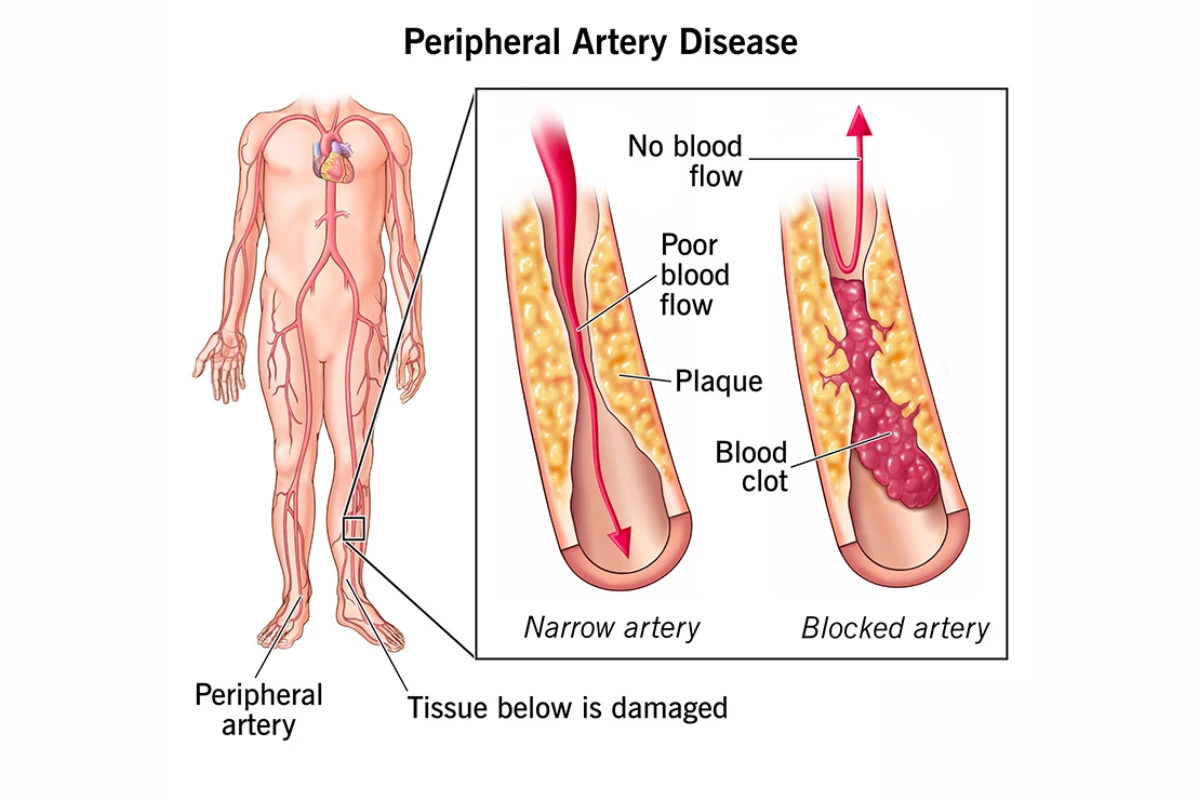
Peripheral Arterial Disease
A circulatory condition where narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs. It often causes leg pain during activity and can significantly affect mobility.
Cause: Narrowed arteries reducing blood flow, often due to atherosclerosis.
Symptoms: Leg pain during walking, cold limbs, and non-healing wounds.
Complications: Gangrene and limb loss.
Treatment: Lifestyle changes, medications, or revascularization procedures.
Pulmonary Embolism
A potentially fatal condition caused by a blood clot blocking a pulmonary artery. It requires immediate medical intervention to prevent severe complications.
Cause: Blood clot in the lungs, usually from DVT.
Symptoms: Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heart rate.
Complications: Lung damage, low oxygen levels, and death.
Treatment: Anticoagulants, thrombolytics, and supportive care.