A pacemaker is a small, life-saving device implanted into the chest to regulate the heart’s rhythm. It sends electrical impulses to the heart when it beats too slowly or irregularly, ensuring that the heart maintains a normal rate and rhythm. Pacemaker implantation is commonly recommended for people with arrhythmias, a condition where the heart beats too fast, too slow, or irregularly.
What is Pacemaker Implantation?
Pacemaker implantation is a procedure in which a small device is placed under the skin of the chest to help control abnormal heart rhythms. The pacemaker consists of a pulse generator (a small battery-powered device) and leads (wires) that connect the device to the heart. The leads deliver electrical impulses to the heart to stimulate a normal heartbeat when necessary.
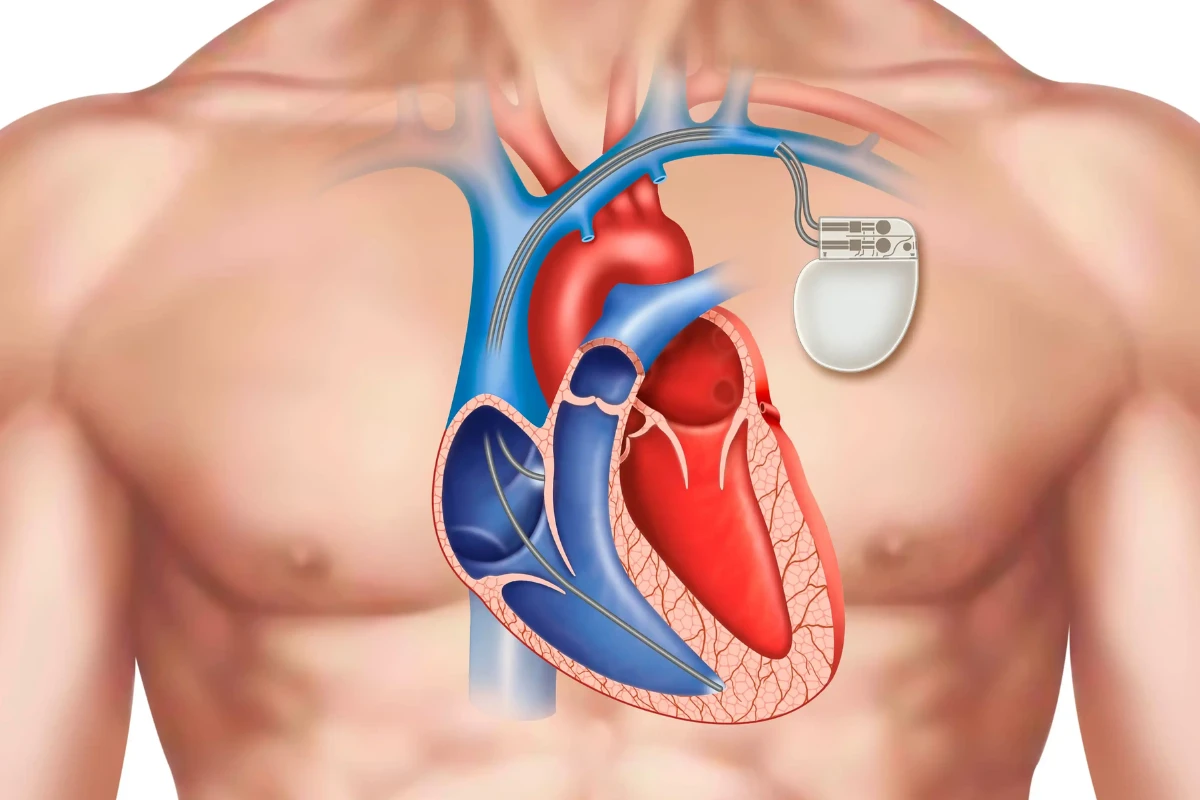
Why Is a Pacemaker Needed?
A pacemaker is usually recommended for individuals with:
- Bradycardia: A condition where the heart beats too slowly (less than 60 beats per minute), causing dizziness, fatigue, or fainting.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation or heart block, that disrupt the heart’s normal rhythm.
- Congenital heart conditions: Heart abnormalities present from birth that affect the heart’s ability to maintain a regular rhythm.
How Is Pacemaker Implantation Performed?
Before the Procedure:
- A thorough medical evaluation is done, including blood tests, an ECG, and sometimes imaging to assess heart function.
- Patients are advised to fast for a few hours before the procedure and inform the medical team about any medications or allergies.
- Sedatives are often administered to help the patient relax, but the procedure is typically done under local anesthesia.
During the Procedure:
- The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and the patient remains awake but relaxed.
- A small incision is made just below the collarbone where the pacemaker will be implanted.
- The leads are inserted through a vein and guided to the heart under X-ray guidance.
- Once in place, the pacemaker’s pulse generator is connected to the leads and positioned under the skin.
- The device is tested to ensure it is working correctly, and the incision is closed.
After the Procedure:
- The patient is monitored for a few hours to ensure the pacemaker is functioning properly.
- An overnight stay in the hospital may be required for observation, depending on the patient’s condition.
- The incision site is checked for signs of infection or bleeding, and the patient is given instructions on how to care for the wound.
Benefits of Pacemaker Implantation
Pacemaker implantation offers several life-improving benefits:
- Regulated heart rhythm: It helps restore a normal heart rate, preventing symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, or fainting.
- Improved quality of life: By maintaining a regular heartbeat, pacemakers allow individuals to engage in everyday activities without fear of heart-related symptoms.
- Prevent complications: Pacemakers reduce the risk of severe complications associated with arrhythmias, such as stroke or heart failure.
Risks of Pacemaker Implantation
Although the procedure is generally safe, there are potential risks, including:
- Infection at the incision site
- Blood clot formation near the heart or in the veins
- Lead dislodgement or malfunction
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung) due to the insertion of leads
- Hematoma (bleeding under the skin)
Post-Procedure Care
- Wound care: Keep the incision site clean and dry. Follow the doctor’s instructions on how to care for the wound and when to remove any dressings.
- Avoid heavy lifting: For a few weeks after the procedure, avoid lifting heavy objects or performing strenuous activities.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular check-ups are necessary to monitor pacemaker function and battery life. A pacemaker checkup typically involves a non-invasive scan to assess the device’s performance.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Patients may be advised to avoid certain electrical equipment or strong magnetic fields, which can interfere with the pacemaker’s function.
Conclusion
Pacemaker implantation is a safe and effective solution for individuals with abnormal heart rhythms. By regulating the heart’s beat, it can significantly improve the quality of life and prevent serious complications. If you or a loved one is considering pacemaker implantation, it’s essential to work closely with us to ensure the best possible outcomes.
